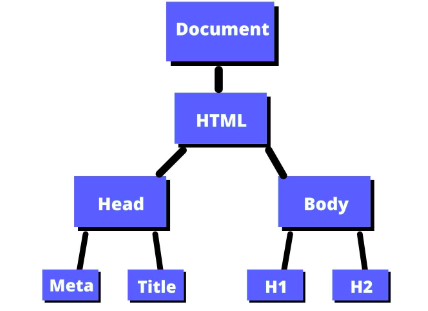
Javascript-Dom :
An analogy to describe JavaScript and its relationship to HTML and CSS:
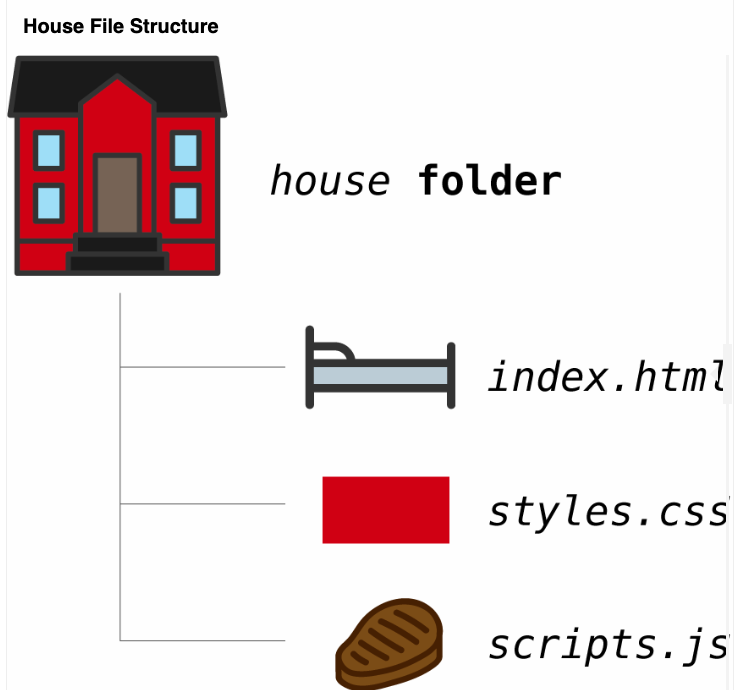
HTML : contains the structure of the page itself. It is kind of like the structure of the building.
CSS file :contains the styling of the page. It allows you to change colors, positioning and more. It is kind of like the design of the building itself.
JavaScript file : determines the dynamic and interactive elements on the page. It determines what happens when users click, hover or type within certain elements. This is kind of like the functionality of the building.
Explain control flow and loops using an example process from everyday life, for example, 'waking up' or 'brushing your teeth' (but not those).
Control flow and Loops : It likes, we are going to theam park and go for the Carnival ride : 1. Ticket booth checks to see if you have any ticket before go for a ride. 2. We continue a ride if we still have ticket. Until we run out of ticket. 4. When we runout of ticket our condition fail and get kick out off the ride.
Loops are used to run the same code over and over untill a certain condition is met.
Describe what the DOM is and an example of how you might interact with it:
Document Object Model (DOM) : When a web page is loaded, the browser creates a Document Object Model of the page.
Object inside DOM : Add script to Element to add, edit, delete and update all event and display to browser right away. Use Javascript to access to HTML DOM by link to ID, class and all tag.
Explain the difference between accessing data from arrays and objects:
Objects : When to Use Objects Objects are used to represent a “thing” in your code. That could be a person, a car, a building, a book, a character in a game — basically anything that is made up or can be defined by a set of characteristics. In objects, these characteristics are called properties that consist of a key and a value.
Arrays : When to Use Arrays We use arrays whenever we want to create and store a list of multiple items in a single variable. Arrays are especially useful when creating ordered collections where items in the collection can be accessed by their numerical position in the list. Just as object properties can store values of any primitive data type (as well as an array or another object), so too can arrays consist of strings, numbers, booleans, objects, or even other arrays.
Explain what functions are and why they are helpful:
Functions : Using a function, it is possible to reduce the size of a program by calling and using the function at different places in the program. Functions help in code modularity, which means that the entire code is divided into separate blocks, each of which is self-contained and performs a different task.